➡ Sundry: Often petty expenses are incurred in a business such as on refreshment, postage, conveyance, etc. Such expenses are normally debited in one account, i.e., Sundry Expenses Account. The Journal entry passed is:

➡ Income Tax: For a sole proprietorship, income tax is treated as drawings of the proprietor because it is neither loss, nor an expense of the business.
(i) When income tax is paid:
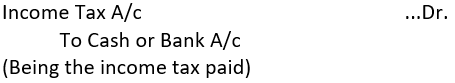
(ii) For treating it as drawings of the proprietor:
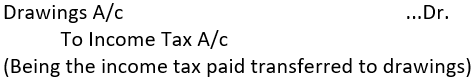
Note: In a partnership firm and joint-stock companies, income tax shall be paid by the partnership firm and joint-stock companies respectively.
➡ Closing Stock: Closing Stock is the goods unsold at the end of the year. It is not given in Trial Balance but is given as an additional information. In order to calculate the correct gross profit or gross loss, it should be brought into the books. Adjustment entry for Closing Stock is as follows:

Remember: Closing Stock is to be valued at cost or net realisable value (market price) whichever is lower.
➡ Outstanding Expenses: Outstanding expenses are the expenses that relate to the current accounting year but have not been paid till the year end. They should be recorded as expense and also payable.
Example: Wages for the Year ended 31st March, 2012 are 6,000. Out of this, ₹ 500 for the month of March, 2012 have been paid in April, 2012, Since, ₹ 500 as on 31st
March, 2012 is yet to be paid it should be recorded in the books by passing the following Journal entry:

➡ Prepaid Expenses: Payment of expenses like—lnsurance, Rent of Shop, etc., are paid in advance benefit of which may expire in the next accounting year. Such expenses are termed prepaid expenses.
Example: On 1st July, 2011, ₹ 1,200 were paid as insurance premium for the shop for the whole year. Final accounts have to be prepared on 31st March, 2012. It means advance payment has been made for the period 1st April, 2012 to 30th June, 2012.
Since, payment relating to the period 1st April, 2012 to 30th June, 2012 relates to the next year, it should be recorded in the books for the year ended 31st March, 2013 as prepaid expenses. Journal entry passed is:

Note: Prepaid Insurance Premium A/c is an asset.
➡ Depreciation: Due to efflux of time or obsolescence or use of fixed assets, value of these assets decreases every year. This fall in value is called Depreciation. It is an expense, hence, trading loss. The following Journal entry is passed for recording depreciation:

➡ Accrued Income: The income which has earned but not received is called accrued income. For example, interest on investment has become due but not received. For accrued income following adjustment entry is passed:

Accrued Income is an asset for the firm. Any increase in asset is always debited.
➡ Income Received in Advance or Unearned Income. Income received but not earned during the accounting period is called income received in advance.
For example, if Building has been given to a tenant on ₹ 2,40,000 p.a. but during the year ₹ 3,00,000 has been received, then ₹ 60,000 will be the income (rent) received in advance. To make adjustment for this, in final accounts following entry should be passed:
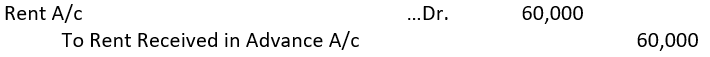
Unearned Income is a liability for the firm. Any increase in liability is always credited.
➡ Interest on Capital: Interest may be allowed on proprietor’s capital. It is an expense for the firm. If interest is allowed on capital, the entry passed is:
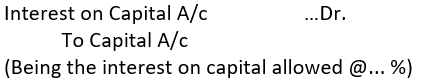
➡ Interest on Drawings: Drawings means withdrawal of cash or goods for personal use by the proprietor. If interest is charged on drawings, it is an income. The entry passed is:

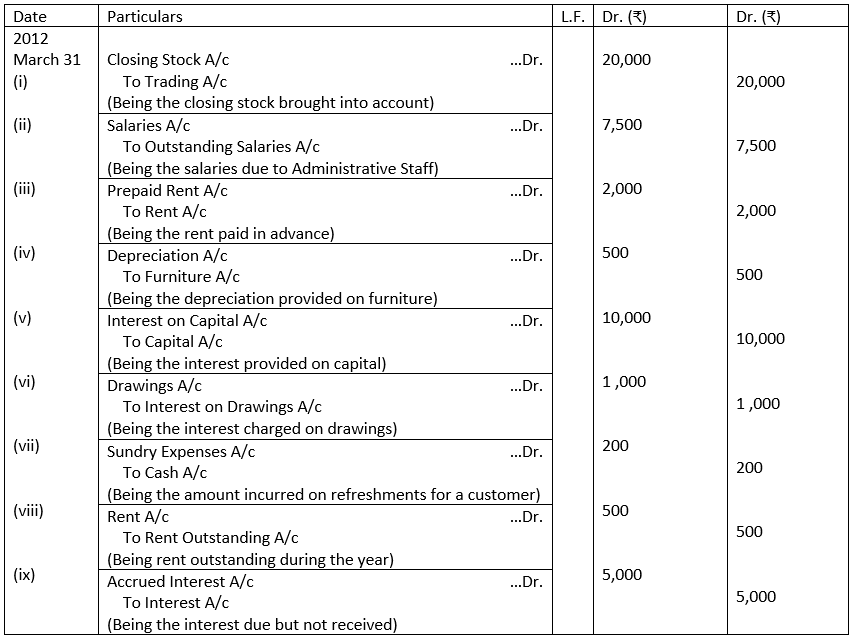
Illustration 14. Pass the Journal entries for the following adjustments as on 31st March, 2012:
(i) Stock at the end of the year ₹ 20,000.
(ii) Salaries due to Administrative Staff ₹ 7,500.
(iii) Out of the rent paid this year, ₹ 2,000 relates to the next year.
(iv) Provide 10% depreciation on furniture costing ₹ 5,000.
(v) Provide 10% interest on capital amounted to ₹ 1,00,000.
(vi) Charge interest on drawings ₹ 1,000.
(vii) Paid ₹ 200 for refreshment for a customer.
(viii) Rent due to landlord ₹ 500.
(ix) Interest due but not received ₹ 5,000.
Solution:
JOURNAL


This is very good website for getting the Right Knowledge at one place in the filed of commerce specialized in Account.