Banking Transaction: Businesses have a Bank Account through which they make and received most of the payments. Payment by cheque, cheque received, withdrawal of cash from bank, deposit into bank, bank charges charged by bank and interest charged on overdraft by bank, etc., are examples of banking transactions. If the books of accounts show debit balance in the Bank Account, it means that such amount is lying deposited in the bank. And if the books of show a credit balance in the Bank Account, it means that such amount is overdrawn and is payable to the bank.
At the time recording banking transaction, the following important considerations should be borne in mind:
1. A Bank Account is a Personal Account and rule of debit and credit for a Personal Account, i.e., ‘Debit the receiver and Credit the giver’ will apply. Whenever a deposit is made in a bank, the Bank Account is debited and whenever a withdrawal is made, the Bank Account is credited.
For example, cash deposit into the bank increases the bank balance. Thus, the Bank Account is debited. Cash withdrawal from the bank reduces the bank balance. Thus, the bank is credited.
2. If a Cheque is received and is not deposited in the bank of the same day, it is debited to Cash Account taking it to be cash. When the cheque is deposited, the Bank Account is debited and the Cash account credited. If the cheque is deposited on the day it is received, Bank Account is Debited instead of Cash Account.
Let us take the Journal entries relating to banking transaction.
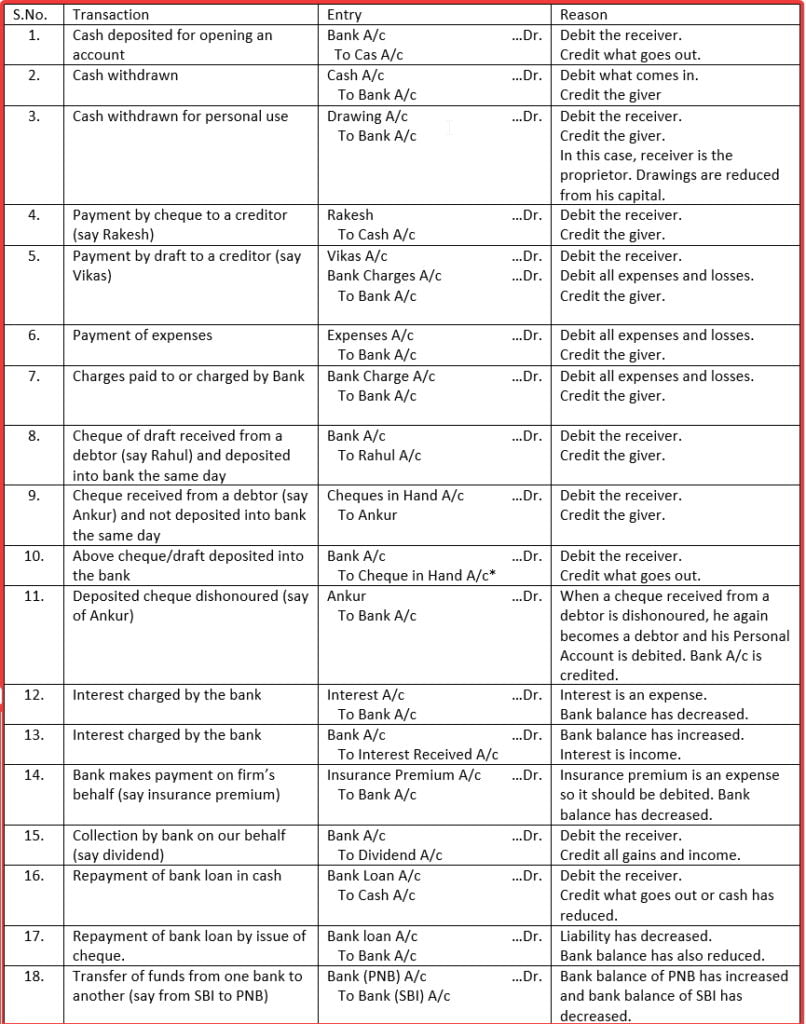
*Cheque in hand is debited because the cheque received has not been deposited into bank the same day. On deposited of cheque into bank, the account is credited.
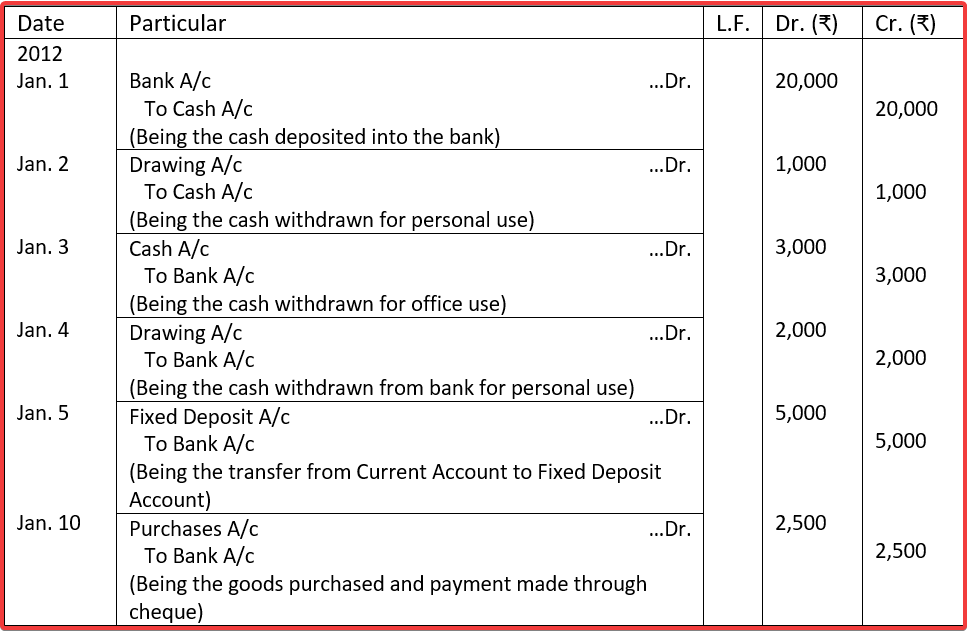
Illustration 5 (Banking transaction). Journalising the following transactions:

Solution:
JOURNAL


This is very good website for getting the Right Knowledge at one place in the filed of commerce specialized in Account.